
When the mean equator and equinox of J2000 are used to define a celestial reference frame, that frame may also be denoted J2000 coordinates or simply J2000. The earlier epoch that was in standard use was the B1950.0 epoch. Since the right ascension and declination of stars are constantly changing due to precession, (and, for relatively nearby stars due to proper motion), astronomers always specify these with reference to a particular epoch. The J2000.0 epoch is precisely Julian date 2451545.0 TT ( Terrestrial Time), or January 1, 2000, noon TT. The standard equinox and epoch currently in use are J2000.0, which corresponds to Janu12:00 Terrestrial Time. Julian epochs are calculated according to: Since 1984, Julian epochs are used in preference to the earlier Besselian epochs. The official constellation boundaries were defined in 1930 using B1875.0.Ī Julian epoch is an epoch that is based on Julian years of exactly 365.25 days. Since the right ascension and declination of stars are constantly changing due to precession, astronomers always specify these with reference to a particular equinox. The previous standard equinox and epoch were B1950.0, a Besselian epoch. Since 1984, Besselian equinoxes and epochs have been superseded by Julian equinoxes and epochs. The period of oscillation of the nutation is 18.6 years.Įquinoxes and epochs Besselian equinoxes and epochs Ī Besselian epoch, named after German mathematician and astronomer Friedrich Bessel (1784–1846), is an epoch that is based on a Besselian year of 365.242198781 days, which is a tropical year measured at the point where the Sun's longitude is exactly 280°. Because he did not have an accurate enough clock, Bradley was unaware of the effect of nutation on the motion of the equinox along the celestial equator, although that is in the present day the more significant aspect of nutation. Bradley published this discovery in 1748. It was first observed by James Bradley as a variation in the declination of stars. Nutation is the oscillation of the ecliptic plane. It is a long term motion with a period of 25,800 years. Precession of the equinox was first noted by Hipparchus in 129 BC, when noting the location of Spica with respect to the equinox and comparing it to the location observed by Timocharis in 273 BC. This is due to precession and nutation, both of which can be modeled, as well as other minor perturbing forces which can only be determined by observation and are thus tabulated in astronomical almanacs. Consequently, star catalogs over the years, even over the course of a few decades, will list different ephemerides. The equinox moves, in the sense that as time progresses it is in a different location with respect to the distant stars. Since that time Julian equinoxes and epochs have been used. Before 1984 Besselian equinoxes and epochs were used. The previous standard equinox and epoch was B1950.0, with the prefix "B" indicating it was a Besselian epoch.

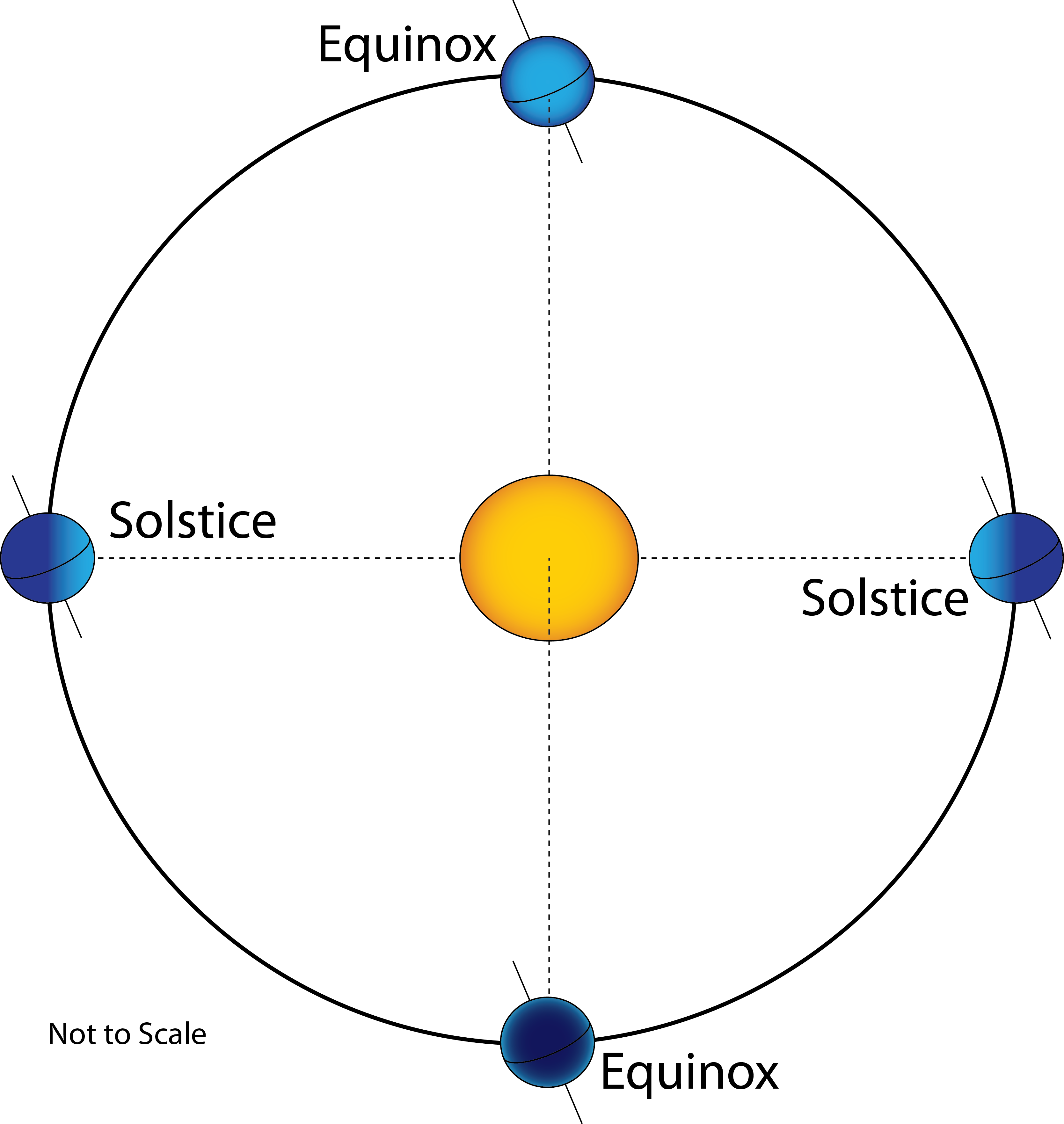
The prefix "J" indicates that it is a Julian epoch. The currently used standard equinox and epoch is J2000.0, which is Januat 12:00 TT. Therefore, a complete specification of the coordinates for an astronomical object requires both the date of the equinox and of the epoch. Astronomical objects show real movements such as orbital and proper motions, and the epoch defines the date for which the position of an object applies. This date should not be confused with the epoch. In a cycle of about 25,800 years, the equinox moves westward with respect to the celestial sphere because of perturbing forces therefore, in order to define a coordinate system, it is necessary to specify the date for which the equinox is chosen. In contrast to the common usage of spring/vernal and autumnal equinoxes, the celestial coordinate system equinox is a direction in space rather than a moment in time. Although there are two such intersections, the equinox associated with the Sun's ascending node is used as the conventional origin of celestial coordinate systems and referred to simply as "the equinox". In astronomy, an equinox is either of two places on the celestial sphere at which the ecliptic intersects the celestial equator. For the moment when the Sun is positioned directly over Earth's equator, see Equinox. This article is about the celestial coordinate system.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
